Design Secrets: Gestalt Theory Similarity Explained
How does Gestalt theory explain similarity?
Gestalt theory explains similarity by suggesting that elements sharing similar qualities, such as shape, color, or size, are perceived as related and grouped together. This principle of similarity helps in organizing visual information and creating a sense of unity among design elements.
Key Highlights
- Gestalt theory is a set of principles that explain how the human brain perceives and organizes visual information
- One of the key is the principle of similarity, which states that the brain groups similar elements together
- Understanding the principles of gestalt theory can greatly improve the user experience in design
- The principle of similarity can be used to create visual hierarchy and organize information in a design
- By applying the principle of similarity, designers can create a cohesive and visually appealing design that is easy for users to understand
- The principle of similarity has various real-world applications in design, such as in web design and mobile app design
Introduction
Gestalt theory is a set of principles that explain how the human brain perceives and organizes visual information. It was developed by a group of German psychologists in the early 20th century and has since become a fundamental concept in design. One of the key principles of gestalt theory is the principle of similarity, which states that the brain groups similar elements together.
When we look at a design, our brain automatically looks for patterns and similarities. It organizes the visual information into groups based on the similarities it detects, which helps us make sense of the world around us. This principle of similarity is crucial in design because it allows designers to create visual hierarchy, organize information, and enhance the user’s attention through close proximity and the use of different shapes.
Understanding the principles of gestalt theory is essential for product designers because it provides a framework for creating cohesive and visually appealing designs. By applying the principle of similarity, product designers can group similar elements together and create a sense of unity and organization in their designs. This not only improves the aesthetics of the design but also makes it easier for users to understand and navigate, especially when it comes to distinguishing between similar items. Now, let’s dive into the concept of gestalt thinking and its seven laws or principles that directly apply to modern product design, and share some examples of how they’re used by product designers.
In this blog, we will explore the principle of similarity in depth and discuss its importance in design. We will also examine real-world applications of the similarity principle and provide examples of how it can be used to enhance the user experience. So let’s dive in and uncover the design secrets of gestalt theory similarity.
Understanding the Gestalt Principles
To understand the principle of similarity, it is important to first have a basic understanding of the gestalt principles. The term “gestalt” comes from the German word meaning “shape” or “form,” and the gestalt principles were developed by German psychologists in the early 20th century.
The gestalt principles are a set of laws that describe how the human eye and brain perceive and organizes visual information. These principles, including similarity, continuation, closure, proximity, figure/ground, and symmetry and order, are based on the idea that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. In other words, we don’t perceive visual elements in isolation, but rather as part of a larger, organized whole. Understanding the gestalt principles of perception, including the law of similarity, is crucial to understanding how the human eye and brain interpret and process visual information.
The gestalt principles explain how our brain processes visual information and groups elements together based on their similarities, proximity, and other factors. They provide a framework for understanding how we perceive visual stimuli and help designers create effective and aesthetically pleasing designs.
One of the key principles of gestalt theory is the principle of similarity. According to this principle, the brain groups similar elements together, even if they are not physically connected. This allows designers to create visual hierarchy, organize information, and guide the user’s attention.
The Origin and Evolution of Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt psychology originated in the early 20th century as a response to the prevailing behaviorist and structuralist theories of psychology. It was developed by a group of German psychologists, including Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka.
The gestalt psychologists believed that the human mind perceives and organizes visual information in a holistic and organized way, rather than as a collection of individual stimuli. They proposed that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts and that our perception is influenced by the relationships and patterns we perceive in the world.
Gestalt psychology challenged the reductionist approach of behaviorism, which focused on studying individual stimuli and their effects on behavior. Instead, the gestalt psychologists emphasized the importance of studying the whole perceptual experience and the role of context and organization in perception.
The principles of gestalt psychology have had a significant impact on various fields, including psychology, design, and visual arts. They provide a framework for understanding how the human mind processes visual information and have been widely applied in design to enhance the user experience and create visually appealing designs.
Core Concepts Behind Gestalt Theory
At the core of gestalt theory is the idea that the human brain perceives visual information as a whole, rather than as a collection of individual elements. This holistic approach to perception is based on the principle that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
According to gestalt theory, our brain organizes visual information into meaningful patterns and structures based on certain principles. These principles include similarity, proximity, closure, continuation, and figure-ground relationship.
The principle of similarity states that the brain groups similar elements together, even if they are not physically connected. This principle allows designers to create visual hierarchy and organize information in a design.
The principle of proximity states that elements that are close together are perceived as being related, while those that are spaced farther apart are perceived as separate. This principle helps designers create visual organization and guide the user’s attention.
The principle of closure states that the brain fills in missing parts of a design or image to create a whole. This principle allows designers to create visual illusions and engage the viewer’s imagination.
The principle of continuation states that elements arranged on a line or curve are perceived as more related than elements not on the line or curve. This principle helps designers create visual flow and guide the user’s eye through a design.
The principle of figure-ground relationship states that the brain distinguishes between the foreground and background elements in a design. This principle helps designers create visual contrast and highlight important elements.
By understanding these core concepts of gestalt theory, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that engage the viewer’s attention and enhance the user experience.
The Importance of Gestalt Principles in Design
The gestalt principles play a crucial role in design as they help create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience. They provide a framework for organizing and presenting information in a way that is easy for users to understand and navigate.
By applying the principles of gestalt theory, designers can create visual hierarchy, guide the user’s attention, and create a sense of unity and organization in their designs.
When users interact with a design that follows the gestalt principles, they are able to easily perceive the relationships and patterns in the visual information, which improves their overall experience.
The gestalt principles help designers create designs that are visually pleasing, intuitive to use, and communicate their intended message effectively. By understanding and applying these principles, designers can create designs that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and user-friendly.
Enhancing User Experience (UX) Through Gestalt Principles
The gestalt principles are essential in enhancing the user experience (UX) through design. By understanding how users perceive visual information, designers can create designs that are intuitive, visually appealing, and easy to navigate.
One of the key ways the gestalt principles enhance UX is by creating visual hierarchy. By using principles such as similarity, proximity, and closure, designers can guide the user’s attention to important elements and create a clear flow of information.
The gestalt principles also help in organizing information in a way that is easy for users to understand and process. By grouping similar elements together and creating visual organization, designers can improve the usability and clarity of a design.
Furthermore, the gestalt principles help in creating a sense of unity and coherence in a design, which enhances the overall user experience. When users are able to perceive the relationships and patterns in a design, they can navigate and interact with it more effectively.
In summary, the gestalt principles are essential in UX design as they help in creating visual hierarchy, organizing information, and creating a cohesive and intuitive user experience.
Applying Gestalt Principles in User Interface (UI) Design
Gestalt principles play a significant role in user interface (UI) design by helping designers create visually appealing and user-friendly designs. By understanding and applying these principles, designers can create a clear visual hierarchy and guide the user’s attention.
One of the key ways gestalt principles are applied in UI design is through the use of visual hierarchy. By using principles such as similarity, proximity, and closure, designers can create a clear visual hierarchy that helps users understand the relationships between different elements in a design.
For example, by using similar colors, shapes, or sizes, designers can group related elements together and create visual organization. This helps users quickly understand the structure of a design and easily navigate through it.
In addition, the gestalt principles help in creating a sense of unity and coherence in UI design. By using principles such as continuity and figure-ground relationship, designers can create designs that are visually pleasing and easy for users to comprehend.
Overall, applying gestalt principles in UI design helps create visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces that enhance the user experience.
Deep Dive into the Gestalt Theory of Similarity
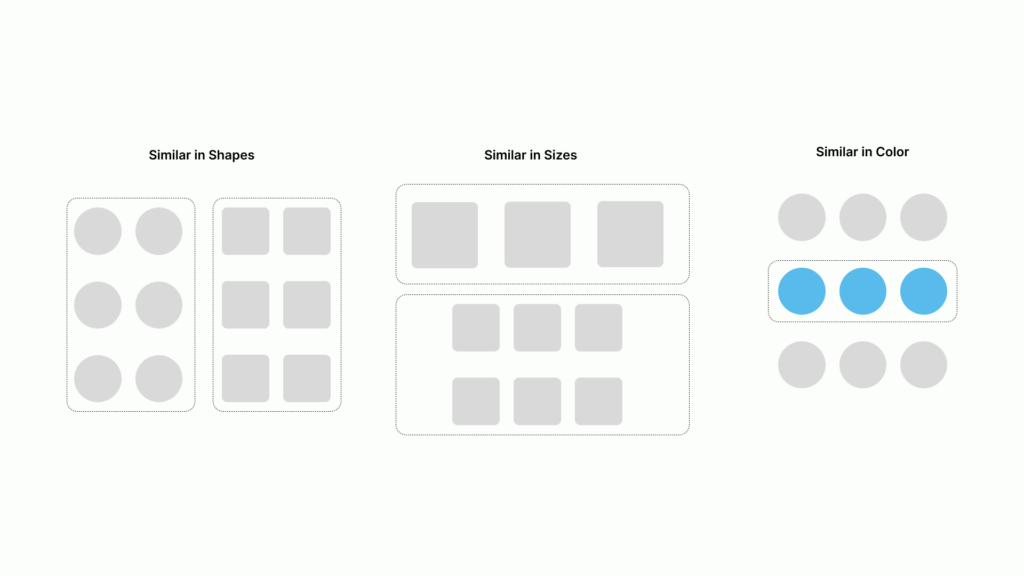
The gestalt theory of similarity is a fundamental principle that explains how the human brain groups similar elements together. According to this theory, when elements share similar characteristics such as color, shape, size, or texture, they are perceived as belonging to the same group.
The principle of similarity allows designers to create visual organization and guide the user’s attention. By using similar elements to group related information together, designers can enhance the user experience and make it easier for users to understand and navigate a design.
Understanding the gestalt theory of similarity is essential for designers as it provides a framework for creating visually appealing and effective designs. By applying this principle, designers can create a sense of unity and coherence in their designs and make it easier for users to process and comprehend the information presented to them. One of the key principles of gestalt theory is the gestalt principle of proximity, which states that objects that are closer together are perceived to be more related. This principle can be applied in various design elements, such as grouping similar elements together or creating a consistent layout. By understanding and utilizing the gestalt principle of proximity, designers can create more cohesive and visually pleasing designs with elements like font size and orientation.
Definition and Significance of Similarity in Design
The principle of similarity is a fundamental design principle that states that the human brain groups similar elements together. Similarity can be based on various characteristics such as color, shape, size, or texture.
In design, similarity is used to create visual organization and guide the user’s attention. By using similar elements to group related information together, designers can create a clear visual hierarchy and make it easier for users to understand and navigate a design.
The principle of similarity is significant in design because it helps create a sense of unity and coherence. When elements share similar characteristics, they are perceived as belonging to the same group and are processed as a whole by the brain.
By understanding and applying the principle of similarity, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience. It allows designers to create visual organization, guide the user’s attention, and make it easier for users to process and comprehend the information presented to them.
Real-World Applications of the Similarity Principle
The similarity principle has various real-world applications in design. By understanding and applying this principle, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience.
One of the key applications of the similarity principle is in creating visual hierarchy. By using similar design elements to group related information together, designers can guide the user’s attention and create a clear hierarchy of importance.
For example, in a web design, using similar colors or shapes for related elements such as buttons or links can help users easily identify and understand their purpose.
Another application of the similarity principle is in creating visual organization. By using similar design elements to group related information together, designers can make it easier for users to process and comprehend the information presented to them.
In summary, the similarity principle has various real-world applications in design, including creating visual hierarchy and visual organization. By understanding and applying this principle, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience.
Gestalt Theory of Similarity in Action
The gestalt theory of similarity is put into action when designers use similar visual elements to group related information together and guide the user’s attention.
By applying the principle of similarity, designers can create a clear visual hierarchy and make it easier for users to understand and navigate a design.
For example, in a website layout, using similar colors, shapes, or sizes for related elements such as headings or buttons can help users quickly identify and understand their purpose.
The gestalt theory of similarity allows designers to create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience. By grouping similar elements together, designers can create a sense of unity and coherence that makes it easier for users to process and comprehend the information presented to them.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Similarity
Several case studies have demonstrated the successful implementation of the gestalt principle of similarity in design. These case studies highlight how designers have used similarity to create visually appealing and effective designs.
Case Study 1: Airbnb
- Airbnb uses the gestalt principle of similarity to group listings with similar characteristics together. By using similar colors, shapes, and sizes for related listings, users can quickly identify and compare their options.
Case Study 2: Apple
- Apple uses the gestalt principle of similarity in its product design. For example, the iPhone’s user interface uses similar visual elements to group related functions together, making it easy for users to navigate and interact with the device.
Case Study 3: Google
- Google uses the gestalt principle of similarity in its search engine results pages. By using similar colors, fonts, and layouts for related search results, users can quickly scan and find the information they are looking for.
These case studies demonstrate how successful implementation of the gestalt principle of similarity can create visually appealing and effective designs. By applying this principle, designers can enhance the user experience and make it easier for users to process and comprehend the information presented to them.
Visual Examples: Before and After Applying Similarity
Visual examples can provide a clear demonstration of the impact of applying the principle of similarity in design. By comparing before and after examples, we can see how similarity can greatly enhance the visual appeal and effectiveness of a design.
Before applying similarity, a design might appear disorganized and cluttered, with unrelated elements scattered throughout the layout. However, after applying similarity, the design becomes cohesive and visually appealing, with related elements grouped together and a clear visual hierarchy.
For example, a website layout might initially have various buttons with different colors and shapes, making it difficult for users to identify their purpose. After applying similarity, the buttons are redesigned using similar colors and shapes, creating a clear visual organization and guiding the user’s attention.
These visual examples illustrate the transformative power of the gestalt principle of similarity in design. By applying this principle, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience.
Complementary Gestalt Principles
In addition to the principle of similarity, there are other complementary gestalt principles that designers can utilize to create visually appealing and effective designs.
The principle of proximity states that elements that are close together are perceived as being related, while those that are spaced farther apart are perceived as separate. By applying the principle of proximity, designers can create visual organization and guide the user’s attention.
The principle of closure states that the brain fills in missing parts of a design or image to create a whole. By using the principle of closure, designers can create visual illusions and engage the viewer’s imagination.
By understanding and applying these complementary gestalt principles, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience.
Exploring the Principle of Proximity
The principle of proximity is a key concept in gestalt theory that states that elements that are close together are perceived as being related, while those that are spaced farther apart are perceived as separate.
In design, the principle of proximity is used to create visual organization and guide the user’s attention. By grouping related elements together and creating spatial relationships, designers can make it easier for users to understand and navigate a design.
For example, in a website layout, using proximity to group related navigation menu items together can make it easier for users to find what they are looking for.
The principle of proximity is closely related to the principle of common region, which states that when objects are located within the same closed region, we perceive them as being grouped together. By using the principle of common region, designers can create visual separation and organization in a design.
Both the principle of proximity and the principle of common region help designers create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience.
Understanding Figure/Ground Organization
Figure/ground organization is a key principle in gestalt theory that states that the brain distinguishes between the foreground and background elements in a design. This principle helps designers create visual contrast and highlight important elements.
Negative space plays a crucial role in figure/ground organization. By using negative space effectively, designers can create a clear distinction between the foreground and background elements, making it easier for users to identify the focal point.
The focal point is the element that stands out visually and captures the viewer’s attention first. By utilizing figure/ground organization and creating a clear focal point, designers can guide the user’s attention and create a visually engaging design.
Understanding figure/ground organization and using negative space effectively can greatly enhance the visual appeal and effectiveness of a design. By creating a clear distinction between the foreground and background elements, designers can create visually appealing designs that capture and hold the viewer’s attention.
Integrating Gestalt Principles into Modern Design
Integrating gestalt principles into modern design is essential for creating visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience.
By understanding and applying gestalt principles such as similarity, proximity, figure/ground organization, and closure, designers can create visually cohesive designs that are easy for users to understand and navigate.
In web design, for example, using similarity to group related elements together, proximity to create visual organization, and figure/ground organization to create visual contrast can greatly improve the user experience.
By integrating gestalt principles into modern design practices, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that engage users and enhance the overall user experience.
Tips for Using Similarity in Web Design
Using similarity in web design can greatly enhance the user experience and create visually appealing and effective designs. Here are some tips for using similarity in web design:
- Use similar colors, shapes, or sizes for related elements such as buttons or links to create visual organization and guide the user’s attention.
- Group related information together using similarity to create a clear visual hierarchy and make it easier for users to understand and navigate the website.
- Use similarity to create visual contrast and highlight important elements, such as the call-to-action button or important messages.
- Be consistent in using similarity throughout the design to create a sense of unity and coherence.
By following these tips and applying the principle of similarity in web design, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience and make it easier for users to process and comprehend the information presented to them.
Leveraging Similarity in Mobile App Design
Leveraging similarity in mobile app design is crucial for creating visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience. Here are some ways to leverage similarity in mobile app design:
- Use similar colors, shapes, or sizes for related elements such as buttons or icons to create visual organization and guide the user’s attention.
- Group related information together using similarity to create a clear visual hierarchy and make it easier for users to navigate the app.
- Use similarity to create visual contrast and highlight important elements, such as the primary action or important notifications.
- Be consistent in using similarity throughout the app to create a sense of unity and coherence.
By leveraging similarity in mobile app design, designers can create visually appealing and effective designs that enhance the user experience and make it easier for users to interact with the app.
Challenges and Solutions in Applying Gestalt Theory
Applying gestalt theory in design can present some challenges, but there are solutions to overcome them. Here are some common challenges and solutions in applying gestalt theory:
- Overcomplicating the design: One challenge is overcomplicating the design by incorporating too many elements. The solution is to simplify the design and focus on the key principles of gestalt theory.
- Lack of visual hierarchy: Another challenge is a lack of visual hierarchy, which can make it difficult for users to understand and navigate the design. The solution is to apply the principles of similarity, proximity, and figure/ground organization to create a clear visual hierarchy.
- Ignoring the user’s perspective: Designers may overlook the user’s perspective and focus solely on the visual aspects of the design. The solution is to consider the user’s experience and how they will perceive and interact with the design.
By addressing these challenges and applying the solutions, designers can effectively apply gestalt theory in their designs and create visually appealing and user-friendly experiences.
Common Pitfalls in Implementing Similarity
Implementing similarity in design can sometimes lead to common pitfalls and design mistakes. Here are some of the common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Overusing similarity: One common pitfall is overusing similarity, which can lead to a lack of visual variety and make the design appear monotonous. To avoid this, designers should use similarity selectively and vary other design elements such as color and shape.
- Lack of contrast: Another pitfall is a lack of contrast between similar elements, making it difficult for users to distinguish between them. To avoid this, designers should ensure that there is enough contrast between similar elements to make them easily distinguishable.
- Ignoring user preferences: Designers may implement similarity without considering the preferences and expectations of the target users. To avoid this, designers should conduct user research and gather feedback to understand user preferences and design accordingly.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls and implementing similarity effectively, designers can create visually appealing and user-friendly designs that enhance the user experience.
Overcoming Obstacles in Gestalt Design Application
Applying gestalt design principles can sometimes present obstacles, but there are practical solutions to overcome them. Here are some common obstacles and their solutions:
- Lack of understanding: One obstacle is a lack of understanding of gestalt design principles. The solution is to study and familiarize oneself with the principles and their applications in design.
- Limited design resources: Another obstacle is limited design resources, such as color palettes or shape libraries. The solution is to be creative and find alternative resources or techniques to achieve the desired design effects.
- Conflicting design objectives: Designers may face conflicting design objectives, such as the need for simplicity versus the desire for visual interest. The solution is to find a balance between the objectives and prioritize the user experience.
By overcoming these obstacles and applying practical solutions, designers can effectively apply gestalt design principles and create visually appealing and user-friendly designs.
The Future of Design: Gestalt Theory’s Role
Gestalt theory will continue to play a significant role in the future of design. As design trends evolve, the principles of gestalt theory will remain relevant in creating visually appealing and effective designs.
In the future, designers will likely continue to utilize the principles of similarity, proximity, figure/ground organization, and closure to enhance the user experience and create cohesive designs.
As technology advances, designers will also explore new ways to apply gestalt theory in emerging design fields such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive media.
Overall, the principles of gestalt theory will continue to shape the future of design and contribute to the creation of visually appealing and user-friendly experiences.
Predictions on the Evolution of UI/UX Design
As UI/UX design evolves, gestalt theory and its principles will continue to play a crucial role. Some predictions on the future evolution of UI/UX design include:
- Increased emphasis on minimalism: UI/UX design will continue to prioritize minimalism, with designers using gestalt principles to create simplicity, clarity, and visual balance.
- Integration of emerging technologies: UI/UX design will incorporate emerging technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and voice interfaces. Designers will use gestalt principles to create seamless and intuitive user experiences in these new mediums.
- Personalization and customization: UI/UX design will focus on personalization and customization, with designers using gestalt principles to create personalized user experiences that adapt to individual preferences and needs.
Overall, the evolution of UI/UX design will see an increased application of gestalt theory and its principles to create visually appealing, intuitive, and personalized user experiences.
Emerging Trends Influenced by Gestalt Principles
Gestalt principles will continue to influence emerging design trends and drive design innovation. Some emerging trends influenced by gestalt principles include:
- Microinteractions: Designers are using gestalt principles to create microinteractions that provide feedback and guide users through interactions with digital products.
- Responsive design: Gestalt principles guide the development of responsive design, ensuring that design elements adapt to different screen sizes and devices while maintaining visual hierarchy and coherence.
- Material design: Material design, influenced by gestalt principles, emphasizes visual hierarchy, depth, and motion to create realistic and intuitive user interfaces.
- Data visualization: Gestalt principles are used in data visualization to organize and present complex data in a visually appealing and understandable manner.
By applying gestalt principles to emerging design trends, designers can create innovative and visually engaging designs that enhance the user experience and push the boundaries of design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Gestalt Theory of Similarity plays a pivotal role in enhancing user experience and interface design. Understanding and applying the principle of similarity can significantly impact the visual appeal and functionality of designs across various platforms. By leveraging this concept effectively, designers can create cohesive and engaging experiences for users. As design continues to evolve, incorporating Gestalt principles like similarity will remain essential for achieving design harmony and usability. To explore further and stay updated on the latest design trends influenced by Gestalt theory, sign up for more insights and resources.
Examples of how similarity can be used in design
Similarity in design plays a significant role in creating a cohesive and visually appealing user experience. Here are some examples of how the principle of similarity can be used:
- Using consistent color schemes throughout a website or mobile app can visually group related elements. For example, a travel app might use shades of blue to represent different categories such as flights, hotels, and attractions. This similarity in color helps users quickly identify and navigate different sections of the app.
- Typography can also benefit from the principle of similarity. Using the same font family, size, and weight for headings and subheadings creates a sense of unity and hierarchy. This allows users to easily scan and understand the content.
- Icons are another area where similarity can be utilized effectively. By using consistent shapes and styles for icons, users can quickly recognize and understand their function. For example, a shopping app might use a shopping cart icon to represent the “add to cart” function, creating a consistent visual language throughout the interface.
| Example | Description |
| Color scheme | Consistent use of color to visually group related elements |
| Typography | Using the same font family, size, and weight for headings and subheadings |
| Icons | Consistent use of shapes and styles for icons to convey function |
These examples demonstrate how similarity in design can enhance the user experience by creating visual cohesion and aiding in the understanding of information.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Gestalt Principles Improve Web Usability?
Gestalt principles can greatly improve web usability by optimizing the design to align with users’ natural visual perception. By understanding how users perceive and process information, designers can create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. Applying gestalt principles such as similarity, proximity, and closure can help users navigate and understand the content more easily, resulting in improved usability and a positive user experience.
Are Gestalt Principles Applicable to Minimalist Design?
Yes, gestalt principles are applicable to minimalist design. In fact, the principles of similarity and proximity are particularly relevant in minimalist design. By using consistent and minimalistic design elements, gestalt principles can enhance the visual clarity and simplicity of minimalist designs. These principles can guide users’ attention to the most important elements, creating a seamless and intuitive user experience.
What Are the Most Common Misconceptions About Gestalt Theory in Design?
One common misconception about gestalt theory is that it is only applicable to visual perception. In reality, gestalt theory can be applied to various design disciplines, including graphic design, user interface design, and even industrial design. Another misconception is that gestalt principles are rigid rules that must be followed strictly. In truth, gestalt principles are a set of guidelines that can be adapted and applied creatively to achieve specific design goals.
How to Start Incorporating Gestalt Principles in Your Designs?
Incorporating gestalt principles in your designs can greatly enhance the user experience and visual appeal. Here are some starting tips to incorporate gestalt principles:
- Start by understanding the basic gestalt principles such as similarity, proximity, and closure.
- Analyze your design elements and identify opportunities to apply these principles.
- Use consistent colors, shapes, and typography to create visual balance and unity.
- Experiment and iterate to find the best implementation of gestalt principles in your design process.
By incorporating gestalt principles into your design process, you can create more cohesive and engaging designs that improve the user experience.
Can Gestalt Theory Be Applied to Non-Digital Design?
Yes, gestalt theory can be applied to non-digital design, including print media, spatial arrangement, and visual communication. The principles of similarity, proximity, and closure can be utilized to create visually appealing and effective designs in various mediums. Whether it’s designing a brochure, a poster, or a physical space, gestalt principles can guide the arrangement and composition of elements to communicate a cohesive message and enhance the overall visual experience.
What Resources Are Available for Further Learning on Gestalt Principles?
There are several resources available for further learning on gestalt principles:
- Books: “The Design of Everyday Things” by Don Norman and “Interaction of Color” by Josef Albers both discuss gestalt principles and their applications in design.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy and Coursera offer courses on design theory and principles, including gestalt principles.
- Design Blogs and Websites: Websites like Smashing Magazine and UX Collective often publish articles and tutorials related to gestalt principles and their practical applications.
- Design Communities: Joining design communities like Dribbble and Behance can provide valuable insights and inspiration from other designers who incorporate gestalt principles in their work.
These resources can help deepen your understanding of gestalt principles and provide practical examples for applying them in your own designs.